Infusion Therapy Institute
960 Rand Road, Suite 224
Des Plaines, IL 60016
Venous Anatomy and Phlebotomy site Selection
It is imperative that the phlebotomist knows the anatomy of a vein and which are the best locations to select.
Arteries deliver oxygenated blood from the heart to the body and the veins return deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart (except, the pulmonary vein).
The difference between Arteries and Veins
Phlebotomy is done on the superficial veins for the extremities. Superficial veins are close to the skin and are often visible to the eyes. The blood in the superficial veins flows slower than blood in the deep veins.
Deep veins runs through the muscles and the blood is forced toward the heart by the squeezing action of surrounding muscles.
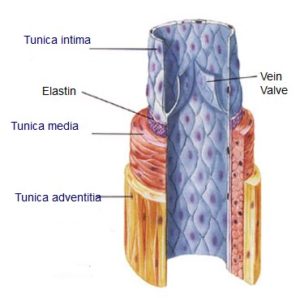
Veins and arteries consist of three main layers:
- Tunica adventitia: It is the outer layer and it is mostly made up of connective tissue.
- Tunica media: Tunica media is the middle layer and it contains of smooth muscle cells and collagen. Smooth muscle cells along with elastic tissue. It is under the control of the sympathetic nervous system. Vasodilation or vasoconstriction occurs to adjusts the diameter of the lumen
- Tunica intima: It the innermost layer. It’s a single layer of endothelial cells and some connective tissue.
- At times, this innermost layer folds to form one-way valves to prevent the blood flowing backward.
Contact Information
(847) 201-2290
info@infusioninstitute.com
In-Person Training Programs
© 2024 Infusion Therapy Institute.

